

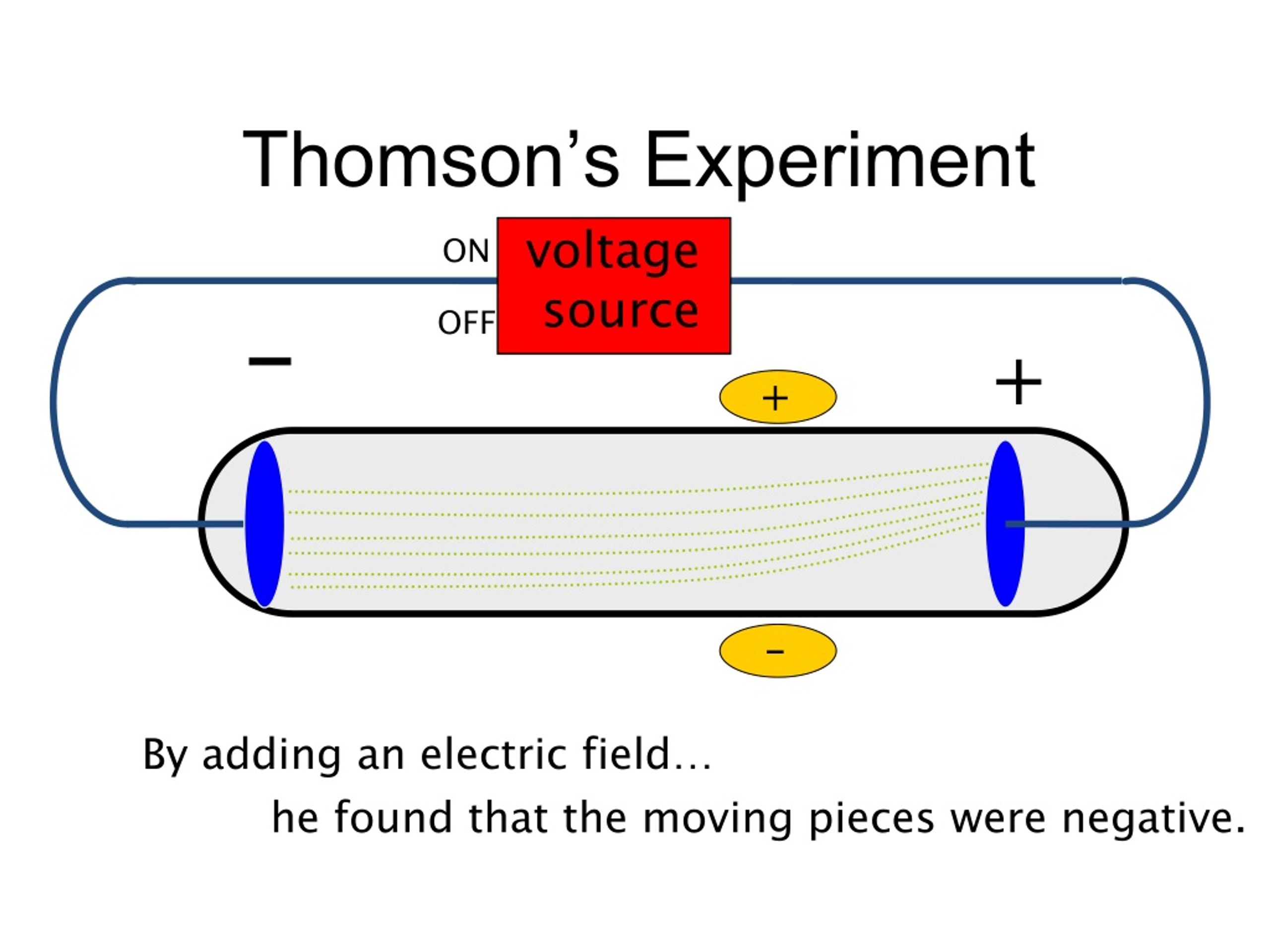
Helps if you know what plum pudding is It is also known as the Chocolate Chip Cookie or Blueberry Muffin Model. Thomson’s Plum Pudding model is a + charge sphere that has (- )charged electrons scattered inside, like “raisins” in “plum pudding”. Since the electrodes could be made from a variety of metals, then all atoms must contain electrons!ġ1 Here are some websites regarding the cathode rayĮxperiment some go beyond what you are accountable for You do not need to visit these websitesġ2 Thomson’s ATOMIC MODEL known as the Plum Pudding Model These electrons had to come from the matter (atoms) of the negative electrode. Thompson Concluded: Cathode rays are made up of invisible, negatively charged particles called Electrons. negative plate Predicted pathway Actual pathway Positive plate Instead, he found that the path curved away from a negatively charged plate and toward a positively charged plate Why? Like charges repel each other, and objects with unlike charges attract each other, Thomson concluded that the stream of charged particles THAT WERE NEGATIVELY CHARGED these particles are called electrons. He predicted that the stream would travel in a straight path. They travel from cathode, across the tube to the anode.Ĩ A diagram of another cathode ray set upĬathode Ray Tubes Thomson put the tube in a magnetic field. When the power is turned on, the electrodes become charged and produce a stream of charged particles. Each electrode is connected to a power source (battery). A cathode ray is a tube that has a piece of metal, called an electrode, at each end.

Used cathode rays to prove that Dalton’s Solid-ball model could be broken into smaller particles Cathode Ray Tubes Cathode rays had been used for some time before Thompson’s experiments. Dalton was the first person to recognize a workable distinction between the fundamental particle of an element (atom) and that of a compound (molecule).ħ JJ Thomson (1856-1940) Cathode Ray Tubes aka billiard ball model Not the model of today Merits of Dalton's atomic theory The atomic theory explains the laws of chemical combination (the Law of Constant Composition and the Law of Multiple Proportions). In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined, or rearrangedĥ A visual of some of Dalton’s postulatesĦ Dalton’s Atomic Model Based on Dalton’s Atomic Theory (6 postulates), most scientists in the 1800s believed that the atom was like a tiny solid ball that could not be broken up into parts. Different atoms combine in simple/definite whole number ratios to make compounds (you can’t have a ½ of a Carbon bonding with Oxygen it’s a whole atom or no atom) 6.
Atoms are indivisible and indestructible 5. All atoms of different elements are different. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same: a) size b) mass c) chemical properties. Democritus model Not the model of todayģ John Dalton (early 1800’s) Dalton’s Atomic Theoryĭalton’s ideas were so brilliant that they have remained essentially intact up to the present time and has only been slightly corrected.Ĥ Dalton’s Atomic Theory aka: 6 PostulatesĪll matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Was the first person to come up with the idea of atom Believed that all matter was composed of indivisible particles he called “ATOMS” Which is derived from the Greek word “Atomos” – meaning indivisible Other philosophers of that time did not agree with his theories. 1 History of Atomic Theory from Democritus to RutherfordĪtomic Structure History of Atomic Theory from Democritus to Rutherford


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
